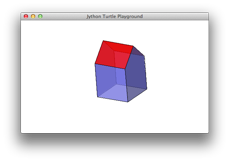
The Source Code
from gturtle import *
from math import *
class Matrix(object):
"""This matrix-class is used to rotate and scale the scene
drawn later. Its mathematical abilities are limited to the
bare necessities to accomplish our 3D-drawing."""
values = [1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]
scale = 25
def multiply_m(self, m):
"""Multply with a new matrix `M'."""
new_values = [0] * 9
for j in range(3):
for i in range(3):
s = 0
for k in range(3):
s += m[k+3*j] * self.values[3*k+i]
new_values[3*j + i] = s
self.values = new_values
def multiply_v(self, v):
"""Apply the current matrix to a vertex or vector."""
v = list(v)
x, y, z = 0, 0, 0
for i in range(3):
x += self.values[i+0] * v[i]
y += self.values[i+3] * v[i]
z += self.values[i+6] * v[i]
return x, y, z
def rotateY(self, angle):
"""Rotate the given angle around the Y-axis."""
s = sin(angle)
c = cos(angle)
self.multiply_m([c, 0, -s, 0, 1, 0, s, 0, c])
def rotateZ(self, angle):
"""Rotate the given angle around the Z-axis."""
s = sin(angle)
c = cos(angle)
self.multiply_m([c, -s, 0, s, c, 0, 0, 0, 1])
def getZ(self, vertex):
"""Return the Z-ordering on the screen of the given
vertex."""
x, y, z = self.multiply_v(vertex)
return x * self.scale
def project(self, vertex):
"""Project a vertex onto the screen's plane and return
the x- and y-coordinates."""
x, y, z = self.multiply_v(vertex)
return y * self.scale, z * self.scale
class Polygon(object):
"""This class represents a polygon in 3D which can be
painted to the turtleFrame. You are responsible yourself
to make sure that the entire polygon is flat."""
def __init__(self, matrix):
self.matrix = matrix
self.vertices = []
self.color = (0.5, 0.5, 1)
self.alpha = 0.75
self.bordercolor = "black"
self.hasborder = True
self.__center = (0, 0, 0)
self.__z = 0
self.__normal = [1, 0, 0]
self.__shadowIndex = 1
def add(self, x, y, z):
"""Add a point to the polygon."""
self.vertices.append((x, y, z))
self.__recalcCenter()
def addArray(self, arg):
"""Add an array with multiple points."""
for pt in arg:
x, y, z = pt
self.vertices.append((x, y, z))
self.__recalcCenter()
def assign(self, polygon):
"""An auxiliary method used for cloning."""
for v in polygon.vertices:
self.vertices.append(v)
self.__recalcCenter()
self.color = polygon.color
self.alpha = polygon.alpha
self.bordercolor = polygon.bordercolor
self.hasborder = polygon.hasborder
def clone(self):
"""Clone the entire polygon and create a copy of it."""
result = Polygon(self.matrix)
result.assign(self)
return result
def translate(self, tx, ty, tz):
"""Move the entire polygon in the direction of (x, y, z)."""
new_vertices = []
for v in self.vertices:
x, y, z = v
new_vertices.append((x+tx, y+ty, z+tz))
self.vertices = new_vertices
self.__recalcCenter()
def __recalcCenter(self):
"""Recalculate the center and the normal vector of the polygon.
These are later used to determine the order of the polygons to
draw those in the back first and to determine the brightness."""
if len(self.vertices) > 0:
mx, my, mz = self.vertices[0]
if len(self.vertices) > 1:
for i in range(1, len(self.vertices)):
x, y, z = self.vertices[i]
mx += x
my += y
mz += z
mx /= len(self.vertices)
my /= len(self.vertices)
mz /= len(self.vertices)
self.__center = (mx, my, mz)
if len(self.vertices) > 2:
v1 = self.vertices[0]
v2 = self.vertices[1]
v3 = self.vertices[2]
w1 = [0] * 3
w2 = [0] * 3
for i in range(3):
w1[i] = v2[i] - v1[i]
w2[i] = v3[i] - v1[i]
n = [0] * 3
n[0] = w1[1]*w2[2] - w1[2]*w2[1]
n[1] = w1[2]*w2[0] - w1[0]*w2[2]
n[2] = w1[0]*w2[1] - w1[1]*w2[0]
n_len = sqrt(n[0]**2 + n[1]**2 + n[2]**2)
if n_len > 0:
for i in range(3):
n[i] = n[i] / n_len
self.__normal = n
else:
self.__normal = [1, 0, 0]
def calcZ(self):
"""Recalculate the `Z'-coordinate of the center, based upon
the current matrix. Note that this `Z'-coordinate does not
correspond to the actual Z-axis but is in respect to the
ordering on the screen."""
self.__z = self.matrix.getZ(self.__center)
n = self.matrix.multiply_v(self.__normal)
m = (n[0] - n[1] + n[2]) / sqrt(3)
if n[0] <= 0:
m = -m
if m < 0:
self.__shadowIndex = 0
else:
self.__shadowIndex = sqrt(abs(m))
return self.__z
def getZ(self):
"""Return the Z-coordinate of the center. Make sure to
recalculate the z-coordinate using `calcZ' first."""
return self.__z
def getColor(self):
"""Return the color, respecting the shadow index and
any transparency."""
if type(self.color) == type((0.5, 0.5, 0.5)):
r, g, b = self.color
else:
c = makeColor(self.color)
r = c.getRed() / 255
g = c.getGreen() / 255
b = c.getBlue() / 255
s = (1 + self.__shadowIndex) / 2
if self.alpha != None and 0 < self.alpha < 1:
return makeColor(r * s, g * s, b * s, self.alpha)
else:
return makeColor(r * s, g * s, b * s)
def draw(self):
"""Draw the polygon and fill it."""
if len(self.vertices) > 1:
points = []
for pt in self.vertices:
x, y = self.matrix.project(pt)
points.append((x, y))
x, y = points[-1]
if self.alpha != 0:
color = self.getColor()
setPenColor(color)
setFillColor(color)
startPath()
setPos(x, y)
for pt in points:
x, y = pt
moveTo(x, y)
fillPath()
if self.hasborder:
setPenColor(self.bordercolor)
setPos(x, y)
for pt in points:
x, y = pt
moveTo(x, y)
mouseAngleX = 0
mouseAngleY = 0
mousePoint = (0, 0)
def getXY(e):
"""Return the coordinates of the mouse-event in turtle-coordintes."""
global playground
pt = playground.toTurtleCoords(e.getX(), e.getY())
return pt.getX(), pt.getY()
def updateMousepoint(x, y):
global mouseAngleX, mouseAngleY, mousePoint
mousePoint = (x, y)
aX = atan2(x, 200)
aY = atan2(y, 200)
rX = aX - mouseAngleX
rY = aY - mouseAngleY
mouseAngleX = aX
mouseAngleY = aY
return rX, rY
def onMousePressed(e):
"""React to whenever the mousebutton is pressed down."""
global mouseAngle, mousePoint
x, y = getXY(e)
updateMousepoint(x, y)
def onMouseDragged(e):
"""React to whenever the mouse is moved with pressed button."""
global mouseAngle, mousePoint
x, y = getXY(e)
angleX, angleY = updateMousepoint(x, y)
rotateMatrix(angleY, angleX)
def rotateMatrix(y_angle, z_angle):
"""Rotate the matrix and redraw the scene."""
global matrix
if y_angle != 0:
matrix.rotateY(y_angle)
if z_angle != 0:
matrix.rotateZ(z_angle)
redraw()
polygons = []
def addPolygon(polygon, translateVector=None):
"""Add an existing polygon."""
global polygons
polygons.append(polygon)
if translateVector != None:
tx, ty, tz = translateVector
polygon.translate(tx, ty, tz)
return polygon
def newPolygon(vertices=None, color=None, alpha=None, hasborder=None):
"""Create a new polygon."""
global matrix, polygons
result = Polygon(matrix)
polygons.append(result)
if vertices != None:
result.addArray(vertices)
if color != None:
result.color = color
if alpha != None:
result.alphe = alpha
if hasborder != None:
result.hasborder = hasborder
return result
def newRectangle(p1, p2, height):
"""Create a new polygon in the shape of a rectangle with the
given height."""
x1, y1 = p1
x2, y2 = p2
vertices = [(x1, y1, 0), (x2, y2, 0), (x2, y2, height), (x1, y1, height)]
return newPolygon(vertices)
def redraw():
"""Redraw the entire scene with all polygons."""
global polygons, playground
playground.clear()
for p in polygons:
p.calcZ()
polygons.sort(key = Polygon.getZ)
for p in polygons:
p.draw()
playground.repaint()
makeTurtle(mousePressed = onMousePressed,
mouseDragged = onMouseDragged)
hideTurtle()
playground = getPlayground()
playground.enableRepaint(False)
matrix = Matrix()
p1 = newRectangle((2, 2), (2, -2), 4)
p2 = newPolygon([(2, 2, 0), (-2, 2, 0), (-2, 2, 4), (0, 2, 6), (2, 2, 4)])
addPolygon(p1.clone(), (-4, 0, 0))
addPolygon(p2.clone(), (0, -4, 0))
newPolygon([(2, 2, 4), (0, 2, 6), (0, -2, 6), (2, -2, 4)], "red")
newPolygon([(-2, 2, 4), (0, 2, 6), (0, -2, 6), (-2, -2, 4)], "red")
redraw()